In the photovoltaic off-grid system, how to calculate and choose the size of DC solar cable?
In the photovoltaic off-grid system, how to calculate and choose the size of DC solar cable?The construction cost of cable engineering in photovoltaic power generation project is generally relatively large, and the reasonable selection of cable type and laying method directly affects the construction cost, so reasonable planning and correct selection of cable model and laying method are the primary link of cable design work. In the photovoltaic power generation system, the selection of the cable is an important part of reducing the cost of power generation.
1.Basic principles of cable selection
The cable selection of photovoltaic power generation follows the general requirements of cable selection, that is, according to the voltage level, the allowable current to meet the continuous operation, the short-circuit thermal stability, the allowable voltage drop, the economic current density and the laying environmental conditions.
At the same time, photovoltaic power generation has its own characteristics, and solar energy systems are often used under harsh environmental conditions, such as high temperature, severe cold and ultraviolet radiation.

Therefore, the following factors should be considered in the selection of cables in photovoltaic systems:
(1) Insulation performance of the cable;
(2) Heat and flame retardant performance of the cable;
(3) Moisture-proof, light-proof (anti-radiation) of the cable;
(4) Cable laying method;
(5) The material of the cable conductor (copper core, aluminum alloy core);
(6)Specifications of cable cross-section.
2. Selection of cables
2.1 Types of photovoltaic power generation cables
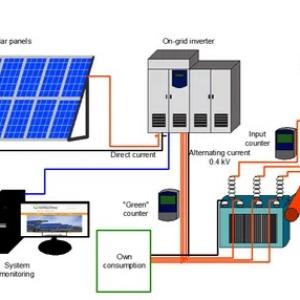
Photovoltaic power generation system cable, according to the photovoltaic power generation system can be divided into DC cable and AC cable, of which the series cable between the components, and the DC cable connected in parallel between the strings accounts for more than half of the cable volume, and the use of AC cable after the inverter.
According to the different application environment, the cables of photovoltaic power generation system can be divided into:
1. DC cable
(1) The series cable between the module and the module, this part should use a special cable with photovoltaic certification.
(2)Rare earth aluminum alloy conductor cables can be used for parallel cables between strings and between strings and DC distribution boxes (combiner boxes).
(3) The cable between the DC distribution box and the inverter, this part can also choose to use rare earth aluminum alloy conductor cable.
The above cables are all DC cables, which are laid outdoors and need to be moisture-proof, sun-proof, cold-resistant, heat-resistant, ultraviolet-resistant, and chemically resistant to acid and alkali in some special environments. The connecting cables between components are usually supplied as a set with the components.
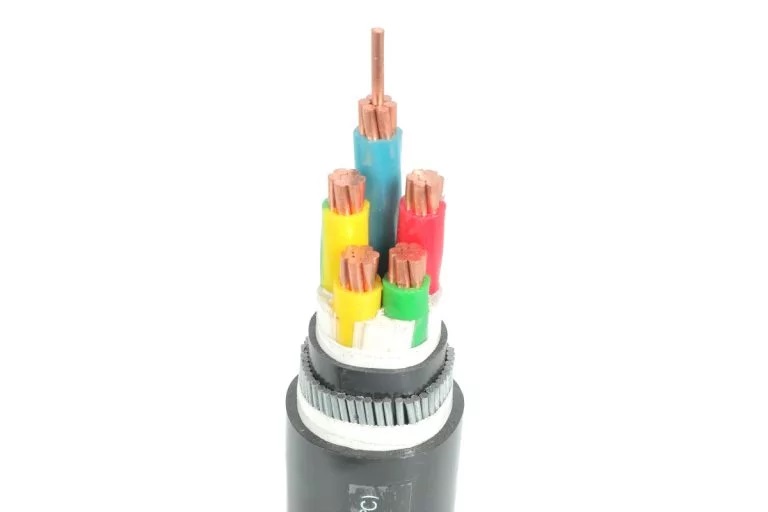
2. AC cable
(1) The connecting cable from the inverter to the step-up transformer.
(2) The connecting cable from the step-up transformer to the power distribution device.
(3) The connecting cable from the power distribution device to the power grid or the user.
This article focuses on the selection and laying of DC cables in photovoltaic grid-connected power generation, and its principles are also applicable to some other types of photovoltaic power generation projects.

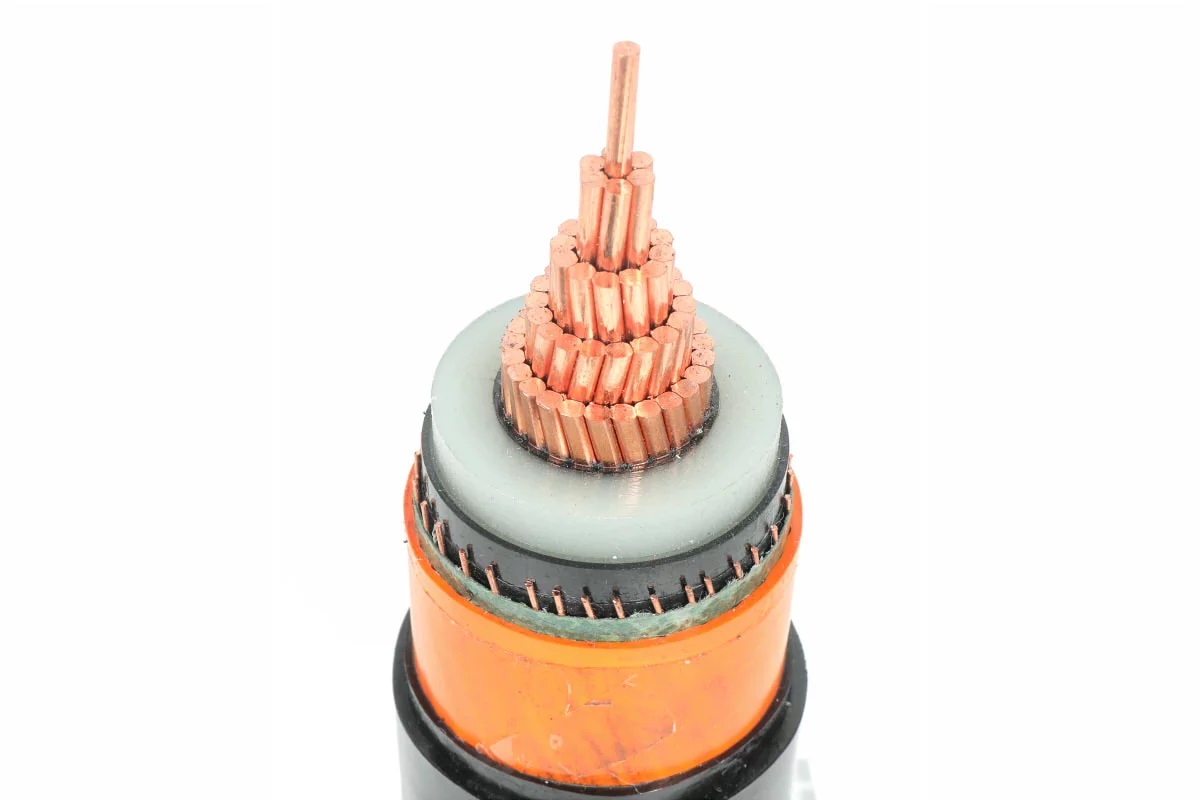
2.2 Photovoltaic special cable
A large number of DC cables in photovoltaic power generation systems need to be laid outdoors, and the environmental conditions are harsh, and the cable materials should be based on UV resistance, ozone, drastic temperature changes and chemical erosion. Long-term use of ordinary cables in this environment will cause the cable sheath to be brittle and even break down the cable insulation. These conditions can directly damage the cable system, increase the risk of cable short circuits, and increase the likelihood of fire or personal injury in the medium to long term, which can greatly affect the service life of the system.
For these reasons, it is necessary to use PV cables and components in solar energy systems. With the continuous development of the photovoltaic industry, the photovoltaic supporting components market has gradually formed, and as far as cables are concerned, a variety of specifications of photovoltaic professional cable products have been developed.
For example, the recently developed electron beam cross-link cable, rated at 120℃, can withstand harsh weather and mechanical impact, is one of the solar cable options. For example, RADOX cable is a kind of solar special cable developed according to the international standard IEC216, and the service life is 8 times that of rubber cable and 32 times that of PVC cable in outdoor environment. Cables and components for solar PV not only offer optimum resistance to weather, UV and ozone damage, but also withstand a wider range of temperature variations (e.g. from -40℃ to 125℃). In Europe, technicians have tested temperatures of up to 100-110℃ on roofs.

During the installation, operation and maintenance of the photovoltaic power generation system, the cables may be routed in the soil below the ground, in the weeds and rocks, on the sharp edges of the roof structure, or exposed to the air, and the cables must withstand pressure, bending, tension, cross-tensile loads and strong impacts. If the cable sheath is not strong enough, the cable insulation will be damaged, affecting the entire service life of the cable or leading to problems such as short circuits, fires, and injury hazards.